|
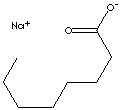
OCTANOIC ACID, SODIUM SALT
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 1984-06-1 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 217-850-5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | CH3(CH2)6COO·Na | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 166.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H.S. CODE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Sodium n-octanoate; Natriumoctanoat (German); Sodium Octanoate; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Octanoato de sodio (Spanish); Octanoate de sodium (French); | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE |
off-white powder |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | soluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | 10 - 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NFPA RATINGS | Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metallic salts of fatty acids (called soap) are primarily used as cleansing agent (mainly sodium- and potassium-) which their molecules attach readily to both polar molecules (of water) and non-polar molecules (of grease or oil). The long hydrocarbon chains are non-polar (and hydrophobic) repelled by water and the salt end molecules are ionic (and hydrophilic) water soluble. Soaps differ according to the type of fatty acid and length of the carbon chain and according to the alkali employed. Fatty acids with longer chains are insoluble. If sodium hydroxide is used as the alkali, hard soaps are formed; potassium hydroxide yields soft soaps. Soap salts are used as insecticides, herbicides, fungicides and algaecides. The lipophilic carbon chains infiltrate and destroy the lipoprotein matrix of the insect's cell membranes. Food grade soap salts are used also as general purpose food additives. Aluminum, calcium, magnesium, lead, zinc or other metals are used in place of sodium or potassium for soaps to be used in industry. Metallic salts of fatty acids are used as stabilizer and plasticizer in plastic industry as well as in cosmetics. They are used as flatting and sanding agents in lacquers, coatings & inks. They can be applied in tablet manufacturing. They are used as drying lubricants and dusting agents for rubbers. They are used as catalysts in chemical synthesis and emulsifiers for emulsion polymerization of synthetic rubber and resin which can be approved for use in food contact applications. They are used as waterproofing additives and ointments. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SALES SPECIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
off-white |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PURITY |
97.5% min (on dry basis) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOISTURE |
5.0% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 25kgs, 1mt in bag in bag | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
OTHER INFORMATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/38, Safety Phrases: 26-37/39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF CARBOXYLIC ACIDS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Carboxylic acid
is an organic compound formed from an alkyl group bonded to a carboxyl group,
-COOH, (a carbon atom is bonded to an oxygen atom by a solid bond and to a
hydroxyl group by a single bond). Examples are shown in table. In substitutive
nomenclature, their names are formed by adding -oic acid' as the suffix to the
name of the parent compound. They can yield two kinds of salts, as they contain
two carboxyl groups in its molecules. Long-chain carboxylic acids are called
fatty acids occuring as esters in fats and oils in nature. Carboxylic acids are
used as solvents and as parent materials to prepare many chemical compounds.
Caproic acid, Caprylic acid, and Capric acid containing the 6-, 8-, and 10-carbon acids respectively are a member of the series of fatty acids found in oils and animal fats. The names of Caproic, Caprylic, and Capric acids are all derived from the word caper (Latin: 'goat'). These are colorless light yellowish transparent oily liquids with unconfortable smells. These are used in organic synthesis, manufacture of perfume, medicine, lubricating grease, rubber and dye. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||